Booths Algorithm Calculator
Did you know?
Booth's Algorithm Division
- A 10X20 exhibit with only one counter produces less sales interactions than a 10’X20′ exhibit with two counters!
- Booth size is relative to the number of staff you should bring and the number of interactions you can expect/handle. A rule of thumb is one staff person per 50 square feet of open exhibit space.
- For every 100 square feet of open space in an exhibit one small 20 inch square podium-sized counter should be available for use by the sales staff.
Booth's Algorithm Calculator

Booth's Algorithm Division Calculator
Booth Calculator Formula:

1. Total Show Attendance X 0.16 = Number of Attendees Interested In Your Product
2. Number of Attendees Interested In Your Product X 0.45 = Number of Visitors to Your Booth
3. Number of Visitors to Your Booth ÷ Number of Hours of the Show = Number of Visitors Per Hour
4. Based on the length of your interactions, determine the Number of Attendees Per Hour that each of your staff can handle.
5. Number of Visitors Per Hour ÷ Number of Attendees Per Hour Per Staff = Optimum number of staff needed for your booth
“The behavior of salespeople and buyers at exhibitions also changes based on how many counters are available in an exhibit. For example, a 10’X20′ exhibit with only one counter produces less sales interactions than 10’X20′ exhibit with two counters. In the exhibits with two counters, the sales staff will have 25% to 60% more sales interactions with attendees.” By Allen Konopacki, CEIR Gurureport.
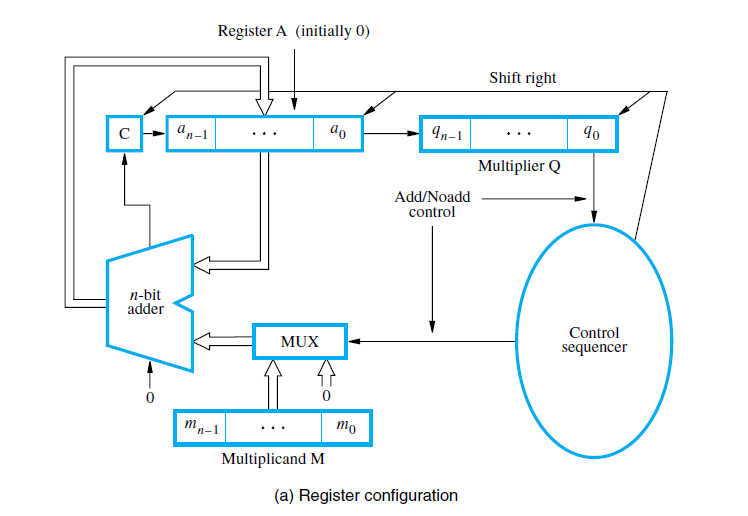
Booth's algorithm examines adjacent pairs of bits of the 'N'-bit multiplier Y in signed two's complement representation, including an implicit bit below the least significant bit, y−1 = 0. For each bit yi, for i running from 0 to N − 1, the bits yi and yi−1 are considered. Where these two bits are equal, the product accumulator P is left. Booth's Algorithm Calculator. Booth’s algorithm is a multiplication algorithm that multiplies two signed binary numbers in 2’s compliment notation. Booth used desk calculators that were faster at shifting than adding and created the algorithm to increase their speed. Booth’s algorithm is of interest in the study of computer architecture. Booth's Multiplier: Booth's multiplication algorithm is an algorithm which multiplies 2 signed integers in 2's complement. The algorithm is depicted in the following figure with a brief description. This approach uses fewer additions and subtractions than more straightforward algorithms.